Introduction
The field of pharmacy is dynamic and multidimensional, with many specialisations that address different patient demands and medical problems. Pharmacists’ responsibilities have grown to encompass direct patient care, prescription administration, and interdisciplinary teamwork as healthcare reforms progress. This article explores a number of important pharmacy specialties, with a focus on paediatrics and oncology but also including other important topics. Knowing these skills can help you forge a rewarding career path, regardless of whether you’re thinking about taking a pharmacy course, earning a bachelor’s degree in pharmacy, or pursuing other pharmacy degrees.
Numerous speciality areas are available in the dynamic and constantly developing field of pharmacy, each customised to the particular requirements of certain patient populations. Pharmacists are becoming more and more important in guaranteeing the best possible patient outcomes through specialised care as healthcare advances. Knowing these disciplines is essential for anyone seeking a Bachelor of Pharmacy (BPharm) or completing a pharmacy course in order to make well-informed career decisions. A degree in pharmacy provides entry into a variety of specialties, each with its own advantages and difficulties, including pediatrics, geriatrics, oncology, and more. This article explores some of the major areas of specialisation in pharmacy, emphasising the responsibilities that pharmacists perform in these fields and their significance. This investigation will give you important insights into the several career pathways accessible in pharmacy, regardless of whether you are thinking about pursuing a Bachelor of Pharmacy or other pharmacy degrees.
1.Pharmacy for Oncology:
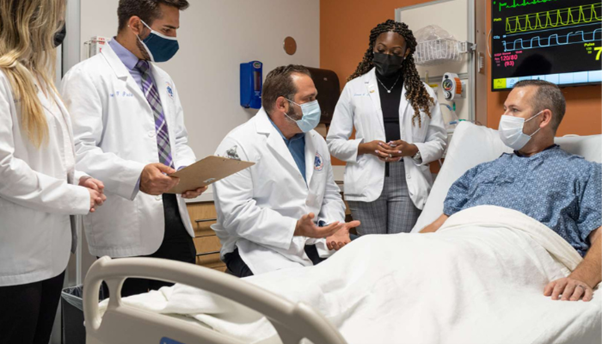
The care of cancer patients is the focus of oncology pharmacies. Experts in the administration of medications for cancer treatment, such as immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and chemotherapy, are oncology pharmacists. Among their responsibilities are:
Medication management: Involves making sure that cancer treatments are administered, scheduled, and dosed correctly.
Mitigating and controlling the negative effects of cancer therapy is known as side effect management.
Patient education: Educating patients about the possible adverse effects of their medications and how to take care of them.
Clinical Trials: Taking part in and overseeing trials for novel cancer therapies.
2.Pediatrics Pharmacy:

The specialty of pediatric pharmacy is the special pharmaceutical requirements of newborns, kids, and teenagers. Pediatric pharmacists have areas of expertise in:
Dosage Adjustments: Determine and modify dosages according to the age, weight, and developmental stage of a child.
Formulation: Developing tablet or liquid forms of medications that are suitable for young patients.
Safety: Making certain that drugs are suitable and safe for young patients.
Education: Teaching parents and other carers how to administer and utilise medications correctly.
3.Advanced Pharmacy:
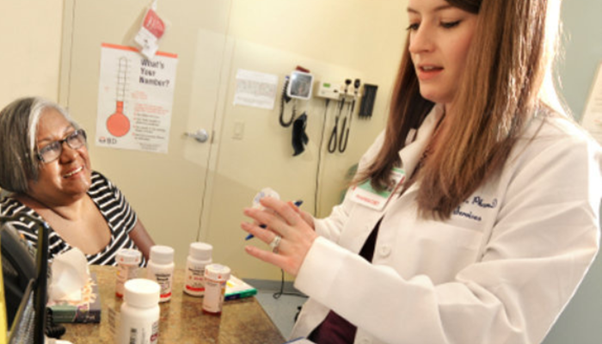
Geriatric pharmacy manages older persons’ complicated prescription needs. A geriatric pharmacists competencies include:
Polypharmacy Management: Managing several prescriptions to prevent drug interactions and negative effects is known as polypharmacy management.
Chronic Disease Management: Taking care of long-term health issues that are frequently experienced by the elderly, include diabetes, arthritis, and hypertension.
Medication Adherence: Helping patients continue to take their medications as prescribed.
4.Pharmacy Practice
Clinical pharmacy include providing direct patient care and coordinating pharmaceutical therapy with other medical specialists. pharmacists in clinical practice:
Medication Therapy Management (MTM): To enhance results, perform thorough assessments of medications.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Create and carry out treatment programmes in conjunction with physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals.
Patient counselling: Give thorough advice on how to take medications and change one’s lifestyle.
5.Pharmacy for Critical Care
The treatment of patients in intensive care units is the main focus of critical care pharmacy (ICUs). Pharmacists that provide critical care:
Emergency Interventions: In cases where life is in danger, administer medication right away.
Complex Therapies: Oversee intricate drug schedules for patients in critical condition.
Monitoring: Pay close attention to how patients are responding to treatment and make any required modifications.
6.Pharmacy for Ambulatory Care
The primary goal of ambulatory care pharmacies is to offer ambulatory patients integrated, easily accessible healthcare services. Pharmacist providing ambulatory care:
Chronic Disease Management: Take care of long-term conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and asthma in an outpatient environment.
Preventive Care: Offer immunisations and health screenings as part of your preventive care services.
Patient Education: Teaching patients about disease management and drug adherence is part of patient education.
7.Pharmacy for Infectious Diseases
Antimicrobial agent use and infection management are the areas of expertise for infectious disease pharmacies. Pharmacists that treat infectious diseases:
Antimicrobial Stewardship: Encourage the sensible application of antibiotics in the fight against resistance.
Preventing infection: Developing and putting into practice infection control strategies is infection control.
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (TDM): Track a drug’s levels to make sure it works and to reduce toxicity.
8.Pharmacy Compounding
Compounding pharmacy is the process of creating customised pharmaceuticals that are appropriate to each patient’s unique requirements. Compounding pharmacist:
Personalised Formulations: Develop original drug formulations, including flavoured drinks, hypoallergenic creams, and transdermal gels.
Non-Standard Doses: Give medicines in amounts that aren’t sold commercially.
Veterinary compounding: Preparation for animal patients is known as veterinary compounding.
The field of pharmacy is broad, with specialisations that respond to the particular requirements of various patient demographics. For each specialisation to maximise patient care and enhance medical results, particular knowledge and abilities are needed. Pharmacists are essential to the healthcare system, whether they are working with old patients in geriatrics, youngsters in pediatrics, or cancer patients in oncology.








