Introduction
A Bachelor of Pharmacy (B.Pharm) degree can lead to a variety of job prospects in the healthcare industries and pharmaceutical companies. As healthcare services and drug advances expand, the demand for B.Pharma graduates stays high. This degree provides students with a thorough understanding of drugs, their uses, and their effects, making them great assets in a variety of professional settings. Whether you want to work in direct patient care, research, regulatory affairs, or sales, there is a career path that is right for you.
One of the most popular job paths for B.Pharma graduates is to become a chemist. Pharmacists play an important role in healthcare since they dispense prescriptions, advise patients on correct pharmaceutical usage, and ensure overall patient safety. They work in a variety of settings, including retail pharmacies, hospitals, and clinics.
Another viable job path is as a pharmaceutical sales representative, where B.Pharma graduates can use their knowledge to market and sell pharmaceuticals to healthcare professionals. This job include developing contacts with doctors and chemists, organising product presentations, and meeting sales targets.
Career or Job Opportunities after Earning a Bachelor of Pharmacy Degree
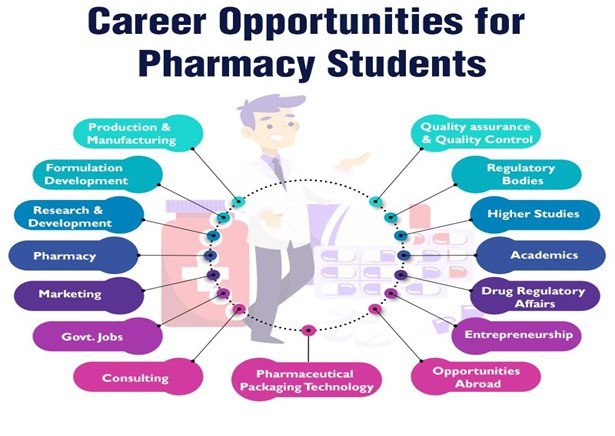
By 2030, the Indian pharmaceutical manufacturing industry is anticipated to be worth US$ 120-130 billion, and US$ 65 billion by 2024. Students who finish a pharmacy course have a variety of job opportunities. Their educational background makes their career opportunities incredibly diversified and adaptable. They may work as a pharmacist or for a pharmaceutical companies. Both the public and private sectors provide several options for students. The government sector may be a career option for you. In addition, you can work for an international company.
Graduates may work at government hospitals, private hospitals, clinics, or private medical businesses. You can also open your own consultation or medical shop.
After completing a B Pharmacy programme, graduates can pursue a range of rewarding occupations, including:
Pharmaceutical Industry:

1. Pharmacist.
One of the most popular job routes for B.Pharma graduates is to become a licenced chemist. Pharmacists play an important role in healthcare by delivering pharmaceuticals, advising patients on correct prescription usage, and guaranteeing their safety. They work in a variety of environments, including retail pharmacies, hospitals, and clinics.
Key responsibilities:
Dispensing prescription drugs.
Offering patient counselling and education.
Monitor patient health and drug therapy.
Ensure the safe and effective use of pharmaceuticals
Skills Required:
Strong understanding of drugs and their effects.
Excellent communication and interpersonal abilities.
Strong attention to detail and problem-solving ability.
2.Pharmaceutical Sales Representative.
Pharmaceutical sales agents, or medical representatives, promote and sell pharmaceutical products to healthcare professionals. They serve as a liaison between pharmaceutical companies and healthcare practitioners, facilitating the acceptance of innovative medications and therapies.
Key responsibilities:
Promoting pharmaceutical products to physicians, pharmacist, and other healthcare professionals.
Organise product presentations and demonstrations
Developing and maintaining client connections
Meeting sales targets
Skills Required:
Strong communication and negotiation abilities.
Excellent awareness of pharmaceutical products and market dynamics
Capability to establish and maintain professional relationships.
Self-motivation and Resilience.
Research and Development (R&D).
3.Pharmaceutical Research Scientist:
A career as a pharmaceutical research scientist can be quite fulfilling for those who enjoy the scientific side of pharmacy. These experts operate in laboratories to create new drugs, improve existing ones, and carry out research studies.
Key responsibilities:
Designing and conducting experiments
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Developing novel pharmaceutical formulations.
Clinical trials to assess drug safety and efficacy
Skills Required:
Strong analytical and problem-solving abilities.
Attention to detail and precision.
Knowledge of laboratory techniques and equipment.
Ability to operate individually and in teams.
4.Clinical Research Associates (CRA)
Clinical research associates manage clinical trials of new medications, ensuring that they conform to regulatory criteria and standards. They play an important role in the development of new drugs and therapies.
Key responsibilities:
Monitoring clinical studies to ensure conformity to procedures
Collecting and analysing trial data
Coordinate with clinical sites and investigators.
Ensure the safety and rights of trial participants.
Skills Required:
Strong organisational and management skills.
Understanding of clinical trial regulations and guidelines.
Strong communication and interpersonal abilities, with a focus on details.
Good documentation and reporting skills.
Regulatory Affairs

5.Regulatory Affairs Specialist.
Regulatory affairs professionals guarantee that pharmaceutical products adhere to all norms and criteria established by regulating organisations. They develop and submit drug approval papers while also staying up to current on regulatory changes.
Key responsibilities:
Preparation and submission of regulatory documents
Ensure conformity with regulatory norms.
Communicating with regulatory authorities
Keeping up with changes in regulations and norms.
Skills Required:
Detailed understanding of regulatory requirements and standards
Strong organisational and documentation skills.
Strong communication and bargaining skills, with a focus on details.
Quality Control and Assurance
6.Quality Control (QC) Analyst.
Quality control analysts evaluate and check pharmaceutical items to ensure they meet quality standards and requirements. They play an important role in ensuring pharmaceutical safety and efficacy.
Key responsibilities:
conducting testing and inspections on pharmaceutical products
Analyse test results and ensure compliance with quality requirements.
Identifying and addressing quality issues
Documenting and reporting findings.
Skills Required:
Strong analytical and problem-solving abilities.
Understanding of laboratory techniques and quality control procedures.
Proficient in documenting and reporting, with a strong focus on detail.
7.Quality assurance (QA). Specialist
Quality assurance professionals guarantee that the methods used in the manufacture of pharmaceutical products adhere to set standards and regulations. They aim to optimise manufacturing processes and avoid quality problems.
Key responsibilities:
Creating and implementing quality assurance policies and processes.
Conduct audits and inspections of manufacturing processes
Identifying and addressing quality concerns
Training employees on quality standards and processes.
Skills Required:
Strong organisational and management skills.
Understanding of quality assurance principles and laws.
Excellent communication and training skills, with a strong focus on detail.
Academics and Education
8.Lecturer / Professor
A career in academics can be rewarding for B.Pharma graduates who enjoy teaching. Lecturers and professors instruct pharmacy students, perform research, and help to enhance pharmaceutical education.
Key responsibilities:
Educating and mentoring pharmacy students
Conducting study and publishing findings.
Responsibilities include curriculum development, committee participation, and academic activities.
Skills Required:
Strong knowledge of pharmacy issues.
Excellent communication and teaching skills.
Ability to undertake research.
Organisational and management skills
Hospital and Clinical Pharmacy
9.Clinical Pharmacist
Clinical pharmacists work in hospitals, partnering with healthcare teams to improve patient pharmaceutical treatments. They provide direct patient care, conduct medication reviews, and verify that medications are used safely.
Key responsibilities:
Reviewing and managing patients’ pharmaceutical treatments.
Working with healthcare teams to optimise treatment plans.
Patients receive medication counselling and instruction.
Monitor patient results and change therapy as required.
Skills Required:
Strong clinical knowledge and decision-making abilities.
Effective communication and interpersonal abilities.
Capable of working as a team and paying attention to detail.
Biotechnology & Biopharmaceuticals
10.Biotech Scientist
B.Pharm graduates can pursue professions in biotechnology and biopharmaceutical companies, developing medications, vaccines, and cures. These scientists use their pharmacy knowledge to create innovative therapies.
Key responsibilities:
conduct research and development of biological goods.
Analysing data and creating new pharmacological formulations
Conducting preclinical and clinical studies.
Working with multidisciplinary teams
Skills Required:
Strong analytical and problem-solving abilities.
Understanding of biotechnology and biopharmaceutical principles.
Requirements include attention to detail and teamwork skills.
Top Companies Hiring B-Pharmacy Graduates
As a B Pharmacy graduate, you can get pharmaceutical work at top businesses both in India and abroad. There are numerous employment openings accessible; all that is required is the perfect combination of talents, dedication, and company to compete. Here are the top 5 pharmaceutical businesses where you can get your preferred job profile:
1. Cipla.
2. Reddy’s Laboratories.
3. Lupin
4. Glenmark Pharmaceuticals
5) Novartis
Conclusion
A B.Pharma degree provides a diverse range of job prospects in the pharmaceutical and healthcare industries. Whether you want to work in direct patient care, research and development, regulatory affairs, quality control, or academia, there is a rewarding career for you. By exploiting your skills and knowledge, you may find the finest employment after B.P harm that matches your interests and objectives. With the increasing demand for healthcare services and the ongoing advancements












